Health Benefits of Vitamin D
Best source of vitamin D is sunlight


Vitamin D Deficiency
The COViD-19 pandemic has touched us all in one way or another, and until a safe effective vaccine becomes widely available, we need to do everything we can to keep ourselves and our loved ones safe. We can start by supporting and strengthening our body's immune system by maintaining a healthy level of Vit D. This is especially important for those of us with dark skin. Due to the current lockdown, access to sunlight is limited, therefore, our ability to top up on the sunshine vitamin is also reduced, and this can have a detrimental effect on our overall health.
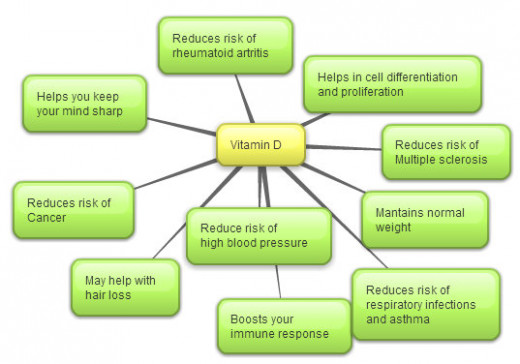
Most of us already know that vitamin D is essential for the maintenance of good health, growth and healthy bones. However, studies suggest that the majority of people still fail to recognise the signs and symptoms of vitamin D deficiency, and do not yet appreciate the significant health benefits we can enjoy by maintaining a healthy level of vitamin D in the body.
Research shows that Vitamin D deficiency can be linked to breast cancer, colon cancer, prostate cancer, heart disease and many other serious conditions. While most people make a point of topping up on vitamin C and E, many are overlooking the importance of vitamin D.
We all live busy lives, and when we get some downtime, many of us prefer to remain indoors. We want to relax and be entertained, so surrendering to the box can be extremely tempting. While the UK is indeed a green and pleasant land for the well-heeled, for the average person there is no real enticement to go out during the winter months. With less exposure to sunlight, we are just not getting enough vitamin D.
On the 29 of October 2012, the UK launched its first National Vitamin D Awareness Week, this was done in an attempt to raise awareness and to better understand the dangers of vitamin D deficiency.
A survey performed by the health pioneering and forward-thinking group, 'BetterYou' found that a large number of the UK population, a massive 9 out of 10 people could be suffering from vitamin D deficiency. Other surveys of UK adults, found that 77 % spent much of their days indoors. Of the UK adults surveyed, two-thirds were deficient in vitamin D, a shocking 71% were diagnosed as 'severely deficient', and took no vitamin D supplements.
Betteryou previously tested over 250 people in the UK for blood serum levels of vitamin D; they found not a single person with a healthy level of vitamin D.
Gone are the days when children played happily outdoors, most of the poorest families are currently living in high rise properties where their free time is spent on computers, playing games or watching TV. Children in the twenty-first century are exposed to less sunlight than did their predecessors, and this lack of exposure to sunlight is having a significant detrimental impact on their health.
Information collected by the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) in the US, found that 9%; a shocking 7.6 million children across the US were vitamin D deficient.
Since 90% of the body's vitamin D comes directly from exposure to the sun, and as little as 10% of our diet, many of us in the Northern hemisphere, are clearly at risk of vitamin D deficiency.
What is Vitamin D?
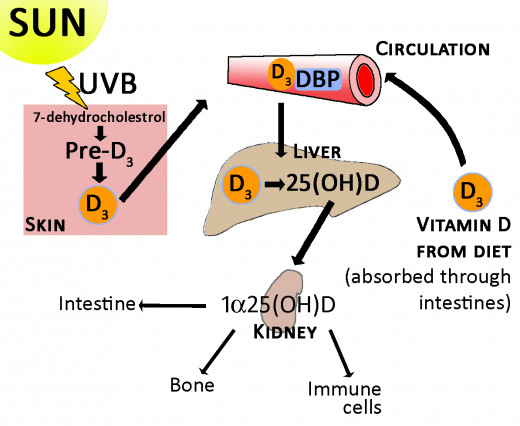
Vitamin D, also known as the sunshine vitamin is a steroid vitamin from the fat-soluble vitamin group, most of which are synthesized by the body from cholesterol when the skin is exposed to the UV rays of the sun. The rest we get from our diet. When insufficient vitamin D is present in the body, the result can be deficiency disease.
Vitamin D is unique; it is not like most vitamins. Our body turns vitamin D into a hormone sometimes called, “activated vitamin D” or calcitriol. As a result of sunlight on the skin, vitamin D is produced and sent to the liver where it is changed into a substance known as 25(OH)D.
When medical tests are performed to ascertain the levels of vitamin D, the results refer to the serum or blood concentration of 25(OH)D and not the amount of vitamin stored in the body tissue.
Vitamin D enhances the intestinal absorption and metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in humans. It enables healthy bone growth, and is important in maintaining healthy teeth and muscles; it prevents rickets in children and Osteomalacia in adults. When taken with calcium, Vitamin D may also help to protect older people from osteoporosis.
Lack of vitamin D can cause bones to become brittle, thin or misshapen.
Vitamin D has many functions that include:
-
Helping to regulate calcium levels in bones, tissue and blood.
-
Immune system regulator helps to fight infection.
-
Neuromuscular function, help maintain healthy heart, circulation, and brain development.
-
Respiratory function for healthy lungs and airways.
-
Reduce Inflammation.
-
Facilitate the absorption of nutrients from the intestine ( calcium and phosphate).
-
Control the amount of calcium in the blood (helps to prevent hypertension).
-
Anti-cancer effects.
Scientists are still trying to understand fully how vitamin D works within the body, and how it affects our overall health. With a wealth of new information coming to light, it is believed that people who are exposed to a reasonable amount of sunlight throughout the year, are receiving sufficient vitamin D, and do not require supplements. However, most of us are not exposed to enough sunlight and are not getting the necessary amount of vitamin D for a healthy body.
So far, there are five forms of vitamin D discovered, and they are known collectively as calciferol; vitamin D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5. But only two forms of D vitamins appear to be most significant to the human body. They are vitamin D2 or ergocalciferol and vitamin D3 or cholecalciferol
Many of us remain confused about the information we receive in regards to the amount of sunlight to which we can safely expose our bodies, before suffering adverse health consequences.
On one hand, we are told we need a certain amount of UV sunlight to maintain a healthy level of vitamin D, but we're also told to reduce our exposure to the damaging effects of the sun. So we slap on the sunblock, cover up and wear large hats In the summertime, but now, we are told to go out and get some sun while it lasts. So how much sun is enough, and how much is too much?
There is no single recommendation for the amount of UV exposure we require to maintain good health, the amount of time we need in the sunlight in order for the skin to make sufficient vitamin D is different for each person. An optimum level of vitamin D largely depends on:
-
The time of the year, even the time of the day will influence the level of UV to which we expose our bodies.
- Located, people who live in the Northern Hemisphere are exposed to less sunlight. The further from the equator we live, the less vitamin D the body can make during the winter months.
- Our skin type and colour, this depends on how dark the skin is, and how easily we get sunburnt. Melanin is a substance that affects the colour of the skin, the more melanin the skin contains, the darker the skin. Melanin protects against skin damage from too much exposure to sunlight. The amount of melanin in the skin affects the amount of vitamin D we produce.
- Our daily activities, people who spend more time outdoors, will make more vitamin D. Short daily periods of sun exposure without sunscreen during the summer months are sufficient for most people to make vitamin D. Studies suggest that the most efficient time of day to produce vitamin D is between 11 am and 3 pm. A short period of 10 to 15 minutes will suffice, for most people.
- Circumstances, for those who can afford to, holidays in a warmer climate can be a good way to top-up on vitamin D during the winter months.
The larger the area of skin that is exposed to sunlight, the higher the chances of making enough vitamin D before causing burns and skin damage. People with darker skin need to spend longer in the sun in order to produce the same amount of vitamin D as those with lighter skin. In the UK, the skin is not able to make vitamin D from winter sunlight between the months of November to March. During the wintry months, there is not sufficient UVB radiation, our Vitamin D comes from what is stored in the body and our food sources.
There are groups of people with intestinal vitamin D malabsorption that may be due to conditions such as Crohn's, Cystic Fibrosis, Kidneys and Liver disease, IBS, bowel resection and gastric bypass surgery. Since vitamin D supplements is not an option for maintaining healthy levels in these cases, UVB phototherapy devices may be useful where the test shows a deficiency in vitamin D.
The debates seem set to run, on the subject of how much Vitamin D we require to maintain good health. As of 2010, the Independent Institute of Medicine recommended that people between the ages of 1-70 should get 600 IUs (International Units) of the vitamin daily, for those 71 years and older, 800 IU daily, for pregnant and lactating women 600 IU daily.
New research suggests adults may need between 1000 - 2000 IU of vitamin D per day to maintain health. However, the recommendation also states that serum 25(OH)D levels of 20 ng/ml are adequate and levels > 50 ng/ml could have a potential adverse effect.
Watch videos (3) for more information on optimum and recommended doses Of Vitamin D.
How much vitamin do we need? From the Office of Dietary Supplements, National Institute of Health
Life Stage
| Recommended Amount
| |
|---|---|---|
Birth to 12 months
| 400 IU
| |
Children 1-13 years
| 600 IU
| |
Teens 14-18 years
| 600 IU
| |
Adults 19-70 years
| 600 IU
| |
Adults 71 years and older
| 800 IU
| |
Pregnant and breastfeeding women
| 600 IU
|
Different Skin Type: Source Vitamin D Council
Skin Type
| Skin Colour
| Skin Characteristics
|
|---|---|---|
I
| White; very fair, red or blond hair; blue eyes; freckles
| Always burns, never tans
|
II
| White; fair; red or blond hair; blue, hazel, or green eyes
| Usually burns, tans with difficulty
|
III
| Cream white; fair with any eye or hair colour; very common
| Sometimes mild burn, gradually tans
|
IV
| Brown; typical Mediterranean Caucasian skin
| Rarly burns, tans with ease
|
V
| Dark Brown; mid-eastern skin type
| Very rarely burns, tans very easily
|
VI
| Black
| Never burns, tans very easily
|
Paler skin types, such as type l to III can produce Vitamin D quicker than type IV to VI
Vitamin D Deficient
The simplest way to diagnose vitamin D deficiency is by blood serum test. The blood serum test can be provided by doctors, or by purchasing a home test kit.
Research shows that a low blood level of vitamin D can be associated with the following:
- The Flu
- Cardiovascular disease
- Cognitive impairment in older people
- Severe asthma in children
- Respiratory diseases
- muscle weakness
- Psoriasis
- Chronic kidney disease
- Diabetes
- Periodontal disease
- Schizophrenia and depression
- cancer
Facts on sources of vitamin D
- The best way to get sufficient vitamin D is to spend 10 to 15 minutes in the sun, the sun provide 90% of the body's vitamin D
- 10% of vitamin D comes from our diet, eat more oily fish and vitamin D fortified foods
- Get Tested for serum Vit D levels
- Take Vitamin D supplements in the winter months. All year round for people who are unable to tolerate sunlight
- Sunscreen makes it harder to make enough vitamin D
- In the US many foods are fortified with vitamin D, compare nutritional labels at supermarket
- For all ages, the RDA of vitamin D is between 600 IU and 800 IU
- Those of us with darker skins and are living in colder climates need more time in the sun and may also need to take vitamin D supplements
Source of Vitamin D
-
Sunshine, as mentioned above, 90% of our vitamin D comes from exposure to sunlight, It is believed that our bodies produce the most vitamin D in the month of June, when the sun is highest in the Northern Hemisphere. However; according to a new study, vitamin D levels in the US peaks in August and bottom out in February. People who believe that they may be deficient in vitamin D should get tested; the best time would be in the month of February when levels are at its lowest.
According to John Cannell, executive director of the 'not for profit' Vitamin D Council, in an article for USA Today, “research shows that some American's vitamin D levels are not adequate in the winter. If they don't supplement, they are going to be deficient” however Cannell apparently, was not involved in the study.
-
The source of the remaining 10% Vitamin D, we get from our diet, but very few foods in nature contain vitamin D, best sources are cod liver Oil and fatty fish, such as salmon, tuna, mackerel, herring, sardines and pilchards.
There are mall amounts of vitamin D in beef liver, cheese and egg yolks. Fortified foods such as milk, margarine, yogurt, some brands of fruit juices and some breakfast cereals, provides much of the Vitamin D in the diet of industrialized countries, like the US, and Canada.
UK milk and dairy products contain little or no vitamin D, only baby formula and margarine are fortified with vitamin D supplements.
Who Needs to Take Vitamin D Supplements?
A mild vitamin D deficiency may not cause major symptoms, but it may cause tiredness and generalized aches and pain. Severe deficiency can lead to osteomalacia (softening of the bone) in adults and rickets in children; there are also links to other conditions such as cancer, asthma, type ll diabetes, high blood pressure, depression, Alzheimer's, autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, Crohn's and Type1 diabetes.
Some people are more at risk of vitamin D deficiency than others and are recommended to take Vitamin D supplements routinely, and they include:
-
All pregnant and breastfeeding women
-
All infants and young children six months to five years
-
People aged 65 and older
-
Individuals who are not exposed to much sunlight
-
People with darker skin, such as those of African Caribbean and South Asian origin
- People with certain kidney, liver or gut diseases
In conclusion, Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to many serious conditions. However, this does not mean that everyone with vitamin D deficiency will get these conditions. People who suspect that they may be Vit D deficient should get as much information as possible from doctors or health care providers. Request a serum test to ascertain the baseline vitamin D levels, the best time to do this is believed to be February to March when levels are at the lowest. Always remember to do as much research as possible, be aware of contraindications.
Watch the public information video no. 3

Video ( 1) Vitamin D for Cancer
Video (2)
Have you suffered from Vitamin D deficiency? If so did you;

© 2013 Jo Alexis-Hagues