Antibiotic Resistance, A Global Crisis In The Making
New strain of antibiotic resistanct gonorrhea an urgent threat says CDC

The Crisis is Already Here
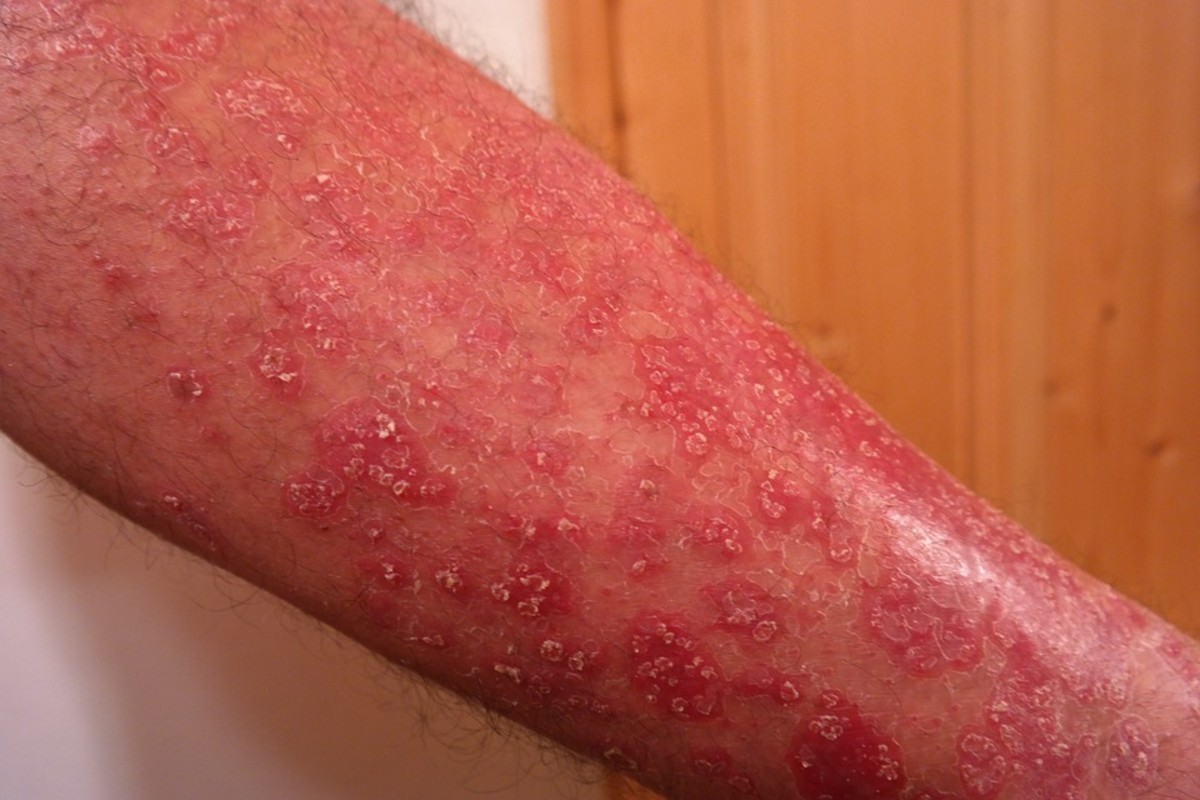
Antibiotic resistant organism threatens many of the advances made in medical treatment over the past 70 years. Drug resistant organisms can significantly affect our ability to fight infection and can have a tremendous impact on chronic diseases like diabetes, asthma, arthritis, pneumonia and many others. The rise in antibiotic-resistant bacteria is no longer a crisis in the making; it is already here.
According to Dr Keiji Fukuda, World Health Organisation's (WHO) Assistant Director-General for Health Security, " without urgent, coordinated action by many stakeholders, the world is headed for a post-antibiotic era, in which common infections and minor injuries which have been treatable for decades can once again kill."
Antibiotics have enabled us to live an average of 20 years longer. Disease-causing organisms once decimated the human population before the discovery of antibiotics.
Until the discovery of bacteria in the 17th century, the knowledge of infection was poor, by the 19th century it was clear that bacteria played a part in causing infection and by the first world war, the need to control infection was fast becoming a priority.
Before the discovery of antibiotics, 93% of soldiers who initially survived an abdominal wound would later die from overwhelming infection.
Antibiotic drugs have enabled doctors to extend and save lives as a matter of course on a daily basis; they help to prevent and cure a range of illnesses that are commonly caused by micro-organisms.
Penicillin contributed to saving countless lives during WW 2. We now take for granted cutting edged surgery that scientists in the era before the 20th-century could only dream about. But we have become complacent, and that complacency has given rise to the emergence of what has become known as the superbugs. Antibiotic resistant organisms are gaining ground even as we twiddle our thumbs.
The discovery of antibiotics remains one of the mankind's most significant medical achievements. Childhood diseases are all but eliminated with the use of vaccines and antibiotics. Before antibiotics, 90% of children with bacterial meningitis died. Among the children that survived, many had severe problems such as deafness and mental disabilities.
Strep throat was once a fatal disease, and a simple ear infection could quickly become dangerous as it spreads to the brain. Tuberculosis, whooping cough, pneumonia are all diseases caused by aggressive bacteria that rapidly reproduce to cause infection and death before the advent of antibiotics unless we take action now; we could be seeing a resurgence of many diseases we thought were now history.
As antibiotic resistance organisms continue to rise, unless we find new antibiotic drugs to replace those that are fast proving to be useless, the future will be bleak. If we fail to put lives before profit, we all lose. The next few years may well see us thrown into a world where microbes rule; those tiny microscopic killers can quickly adapt to most of the commonly used antibiotics we currently have in our arsenal.
We need new antibacterial drugs to combat the global crisis that is facing us. Unless the pharmaceutical companies can come up with new drugs, we may find ourselves in a situation where there is no real protection for humanity as the superbugs take hold, and quickly mutate, making current antibiotics useless while we discuss what strategy to adopt against these microscopic fiends.

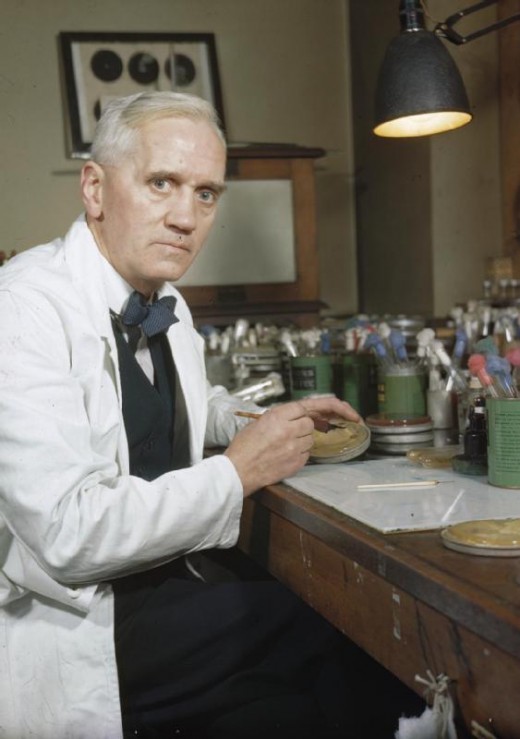
Alexander Fleming

Penicillin Mould

The Discovery of Penicillin
Alexander Fleming was a Scottish biologist, pharmacologist and botanist. He shared the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1945 with Ernst Boris Chain and Howard Florey.
Fleming discovered the first antibiotic in 1928, at St Mary's Hospital London. The discovery happened quite by chance, a happy accident? Or maybe a gift from above. The discovery of penicillin led to the introduction of many more complex antibiotics that continues to save lives today by reducing the number of deaths from infection.
Fleming worked in an exceedingly untidy lab environment, and on his return from a vacation, the scientist found a chunk of mould growing on a dirty dish in his lab. However, to his great surprise, there was no bacterial growth around the mouldy blob. Fleming reasoned that there must be something in the mould that was killing off the bacteria. He would later name the substance, penicillin, a drug still in use and led to the group of medicine we now know as antibiotics.
However; like all medication, the newly discovered penicillin, also came with a warning. The man who gave us the drug also saw the potential for its misuse in the future and stated. "The time may come when penicillin can be bought by anyone in the shop. Then there is the danger that the ignorant man may easily underdose himself and by exposing his microbes to non-lethal quantities of the drug make them resistant."
We failed to heed the warning and may now have to pay the ultimate price.
Drug Resistence, Do You Know the Risk?
Before reading this article, were you aware of the risk of antibiotic resistant bacteria
What are Antibiotics?
The term antibiotic means “against life,” the life, in this case, refers to microbes.
There are many different types of antibiotic drugs in use today:
-
Antibacterials
-
Antivirals
-
Antifungals
-
Antiparasitics
Some antibiotics are effective when used against many organism, and are known as broad-spectrum antibiotics, then there are the narrow spectrum antibiotics that affects fewer organisms. The most commonly used antibiotics are the antibacterials.
Most of us have taken antibiotics in one form or another, at one time or another. These medications were once handed out like smarties, they were prescribed for colds and flu that were most often caused by viral infections, antibacterial drugs would be useless against such infections.
Infectious diseases continue to be the leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for 33% of the 52 million deaths each year, yet, new classes of antibiotics remain scarce.
From 1940 to 1962 an excess of 20 new classes of antibiotic drugs were placed on the market. However, since then, only two new classes of antibiotics have entered the market. The reasons for this lack of progress is three-fold:
- Scientific the easiest ideas have been used, subsequent drug screens for new antibiotics, appears to go round in circles with the same main compound being re-discover. The low hanging ripe fruits have already been picked.
- Economical, finding new antibiotics are time consuming and expensive, yielding a poor return on investment when compared to other more lucrative classes of drugs.
- Regulatory, the process of approval through regulatory bodies such as the U.S. FDA can be a long protracted and confusing process.
In the intervening period, the world has changed, and diseases that were once restricted to certain areas geographically, are now reaching regions that were once thought to be safe. As people travel and move around the globe, diseases such as cholera, tuberculosis and malaria that were once thought to be subdued and conquered are fighting back. We were reminded of how quickly a deadly disease can spread across borders with the recent out-break of the Ebola virus.
Campylobacter
Natural Alternative May be the Way to the Future
Antibiotic misuse and Resistance
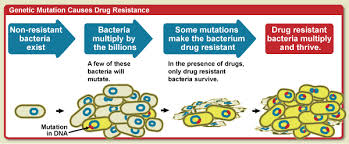
One of the major global health care problems facing us in the 21st century is serious antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. Research suggests that bacteria has developed resistance to many different classes of antibiotics discovered to date.
The number of new antibiotics that are licensed for human use are now less than in the past. Governments and the pharmaceutical industry are failing to invest in the resources needed to produce the next generation of antibacterial drugs.
In some cases, pharmaceutical companies have not only failed to invest in new antibiotics, but they have terminated programs into this type of research for economic reasons.
Antibiotics are drugs that are designed to kill the bacteria that causes infection. However, when an individual take antibiotics, although the drug kills the sensitive bacteria, resistant bugs can be left to grow and multiply. When we use antibiotics repeatedly or do not take it as directed, i.e. not completing a course of drugs because the symptoms of the problem have gone away, we are contributing to the production of drug-resistant bacteria. In the European Union, 2 million people are infected with antibiotic-resistant bacteria, 25,000 patients die from the infections each year.
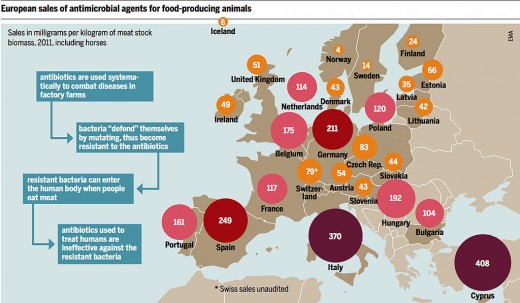
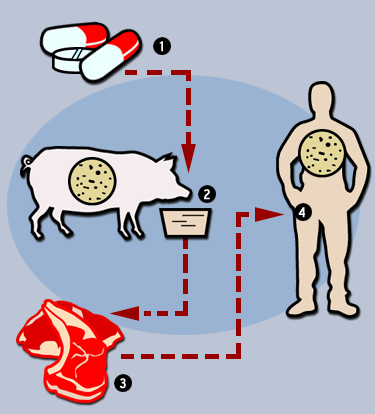
Antibiotics in our food is a major problem. While the use of drugs in the animals we use for food is regulated in almost all countries to help prevent contamination, overuse of antibiotics in animals is a problem that can no longer be ignored. Says a spokesperson for the food safety director for The Center for Science in the Public Interest (CSPI).
The misuse of antibiotics in the human population remains a real problem, the volume of antibiotic drugs sold for use in the livestock industry is staggering. The meat and poultry industry accounts for 80% of all antibiotics sold in the US.
Antibiotics are used in animal feed to achieve faster growth since scientists in 1950, found that by adding antibiotics to animal feed they were able to increase the rate of growth. The drugs are also given to prevent diseases, especially in intense farming, where animals are kept in cramped, unhygienic condition.
As consumers, we all have a say in what we buy and where we shop. Some of the largest supermarket chains are offering organic meat and poultry from livestock not fed antibiotics.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Congress have been urged by consumer advocacy groups and experts, to place a ban on the use of antibiotics in animal feed. The move was opposed by the large companies with the most to lose economically. A federal court of Appeals recently ruled that the FDA may continue its policy of allowing the widespread antibiotics used in animal feed. The court rejected two petitions challenging the use of antibiotics in the feed of animals that are destined for human consumption. According to advocacy groups, 18 out the 30 antibiotics fed to livestock pose a high risk to human health.
How Drug Resistance is Transferred From Farm Animals to Human
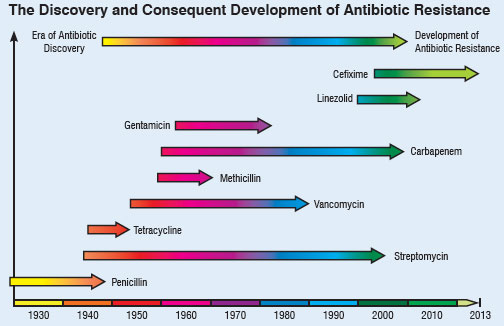
Some of the Antibiotic Resistant Organisms with the Largest Impact on Human Health
Antibiotic Resistant Organisms most urgent and serious threats
| Infection/year
| Healthcare Cost/year
| Estimated Number of Deaths/year
| Threat Level
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Clostridium Difficile (C difficile), not shown drug resistance but included in CDC's report, can cause fatal healthcare-acquired infections (HAIs)
| 250,000
| $1 billion
| Linked to 14,000
| Urgent
|
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, (CRE) are gram-negative bacteria that are almost immune to a class of antibiotics known as carbapenem. Referred to as 'nightmare bacteria' more dangerous than MRSA. Some CRE bacteria are resistant to all existing antibiotics.
| More than 9,000 infections are contracted in hospital (HAI).
| More than 50% of patients infected with CRE die due to a lack of effective antibiotics to help fight the infection.
| Urgent
| |
Drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae
| 820,000 est. number of cases per year, 30% resistance to any antibiotic.
| Urgent
| ||
Floconazole-resistant Candida is a fungus,
| 46,000
| $6000 to 29,000 in direct care cost for extra time in hospital. Total add to health care expenditure per year 8 billion.
| Approx. 35% mortality
| Serious
|
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus (MRSA).
| The most serious MRSA infections are associated with health care, 85% while 14% are community acquired. Serious MRSA infections 80,461.
| 11,285
| Serious
| |
MultiDrug-Resistant Acinetobacter
| Multidrug resistant 7,300, Acinetobacter infections/year 12,000
| 500
| Serious
| |
Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus (VRE)
| 20,000 drug-resistant enteroccoccus infections, 66,000 enterococcus infection/year
| 1,300
| Serious
| |
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
| 6,700 multidrug-resistant pseudomonas infections, 51,000 pseudomonas infections/year
| 440
| Serious
|
According to the CDC, 2 million people get antibiotic resistant infections each year, as many as 23,000 die due to a lack of effective antibiotics to stop the infection. While antibiotic resistant infection can develop anywhere, research show that i
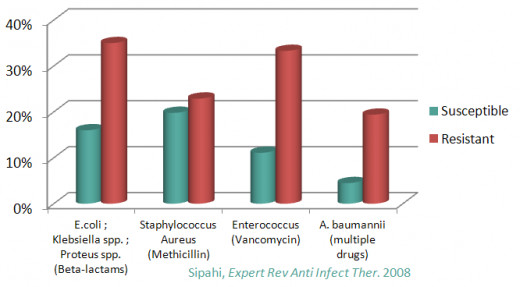
MRSA, 85% Associated with Health Care
References
http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013
http://www.beuc.org/publications/beuc-x-2014-043_p
http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antibiotic_resistance
http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/fleming-lecture.pdf